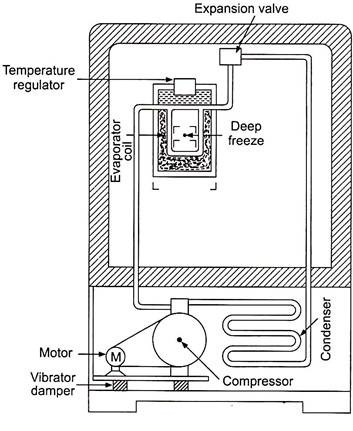
The various parts of a domestic refrigerator are:
1. Compressor
2. Condenser
3. Capillary tube
ADVERTISEMENTS:
4. Evaporator
6. Thermostat temperature control and “off – on” switch.
7. Space for shelves
8. Suction line
ADVERTISEMENTS:
9. Discharge line
In a domestic refrigerator condenser is generally provided at the back of the refrigerator.
Working: The domestic refrigerator works on vapour compresses system. It flows diagram has been shown in Fig. 6.5.
It shows, the refrigerator compressor which compresses the refrigerant vapour (generally freon-12) and discharges it to the air condenser coils (generally provided at the back of the refrigerator), where it dissipates its latent heat and is converted into liquid form. Now this liquid refrigerant is made to pass through the capillary tube (In modern domestic refrigerators, capillary tube is used in place of expansion value) and then it enters in the evaporator coils.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The liquid refrigerant at a very low temperature enters into the evaporators coils; absorbs its latent heat form the surroundings of the evaporator coils and is converted into the vapour form. It further goes to the accumulator which gives the vapours of the refrigerant to compressor during its section stroke.
This way the cycle is repeated again and again. During each cycle the liquid refrigerant absorbs its latent heat from the surrounding of the evaporator coils, and thus the temperature of evaporator coils become very low. If the water is placed inside the evaporator, it will freeze to ice.
The space beneath the evaporator is meant for the shelves to be provided for the storage of eatables, fruits, vegetables etc. to be preserved.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
It is suggested that in the refrigerator hot things should not be placed as it will create an extra load on the refrigerator. If the hot material is placed inside the refrigerator, naturally, the compressor will have to work more to dissipate the extra quantity of heat, which could be avoided if the material is cooled down before it is placed in the refrigerator. The hot material placed inside the refrigerator may spoil the inside surface of the refrigerator.
Fig. 6.4 Domestic Refrigerator