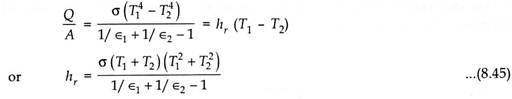The radiative heat exchange between two systems (surfaces) is generally calculated from the simplified equation-
The factor hr is called the coefficient of radiant heat transfer from solid to solid and is expressed in W/m2-deg temperature difference between the enclosed and enclosing surfaces.
The value of hr can be calculated from the heat flux equation for any configuration. For example, the value of hr for the case of two large parallel plates would be-
There occurs simultaneous heat exchange due to radiation and convection in many situations of engineering importance such as-
(i) The heat loss from a hot steam pipe passing through a room,
(ii) The heat loss from hot combustion products when they pass through a cooled duct.
The total heat transfer by both convection and radiation is then obtained by the linear superposition of heat fluxes due to these modes. That is-
ADVERTISEMENTS:
q = qc + qr
For a hot gas at temperature t passing through a duct with wall temperature tw, we may write –
The radiation heat transfer coefficient is a strong function of temperature in contrast to convective heat transfer coefficient.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Example 1:
A pipe with a surface temperature of 480 K is kept within a large enclosure whose walls are at 380 K. Presuming the pipe surface to be black, calculate the coefficient of radiant heat transfer. If the heat transfer coefficient including the effect of radiation and convection is 34.9 W/m2-deg, find the convective heat transfer coefficient.
Solution:
The rate of radiant interchange between the pipe and the walls of the enclosure is –
Example 2:
A hot water radiator of overall dimensions 2.5 m × 1.25 m × 0.25 m and having surface temperature of 335 K is being used to maintain the room temperature at 290 K. Calculate the coefficient of radiant heat transfer, convective heat transfer coefficient and the heat loss from the radiator due to both convection and radiation.
The radiations are considered close to that of a black body and the convective heat transfer coefficient is prescribed by the relation –
hcon = 1.32 (ΔT)0.33 W/m2-deg
ADVERTISEMENTS:
For convection, the actual surface area of the radiator is twice the area of its envelope.
Solution:
Area of the radiator –